本系列文章为学习arcgis for JavaScript v4.x的学习笔记。
监控属性
使用watch(property, callback)进行属性的监控,它会随着属性的变化实时执行。更重要的是,它可以用来监控嵌套属性:
1 | // Creates a new Map with a 'streets' basemap |
也可以同时对多个属性进行监控:
1 | view.watch("center, scale, rotation", function(newValue, oldValue, propertyName) { |
在为属性添加了监控之后,应该将结果保存起来,以备以后在适当的时候清除掉这些监控:
1 | var viewHandles = []; |
属性的监控并不是当属性发生变化之后立即调用监控函数,相反,当一个属性被监控,当他发生变化后,Accessor 便会稍后发起监控函数的调用。因此,实时频繁变化的属性,如view.scale可以不用函数节流而直接监控。
1 | // Divides the view.scale three times |
esri也为我们提供了一个watchUtils模块,方便对属性的监控。
不是所有的属性都能被监控,如esri/core/Collection的属性,对于esri/core/Collection的监控主要是针对其item的added, moved, 或者 removed 。提供的事件有:after-add,after-changes,after-remove,before-add,before-changes,before-remove,change。
Promise
The better you understand promises, the more equipped you’ll be to write cleaner code when working with asynchronous operations in your applications.
promise代表将来从异步任务中返回的值。任务成功调用then中注册的resolve,任务失败调用otherwise。对于Chaining promises即后一个任务要在前一个任务结束之后才能进行,使用then可以将原来的嵌套callback写成优雅的链式代码,还有一种方式是使用await,它可以将异步逻辑以同步的代码形式展现出来。
ArcGIS API for JavaScript的许多方法都返回Promise,esri/tasks下的所有模块和esri/geometry/geometryEngineAsync模块都返回Promise。
不是只有方法返回Promise,很多类本身就是Promise,这样的类有:MapView,SceneView,ViewAnimation,LayerView,All layers。这就意味着可以在类的实例上直接调用then方法,如可以直接在MapView的实例上调用view.then(),表示当MapView准备好之后去执行view.then()中的代码。
Promise VS Event listeners
promise的then方法和事件监听器的行为非常类似。那它们有什么区别呢?Promise允许你在异步处理完成后直接访问其结果,相反,如果你在事件已经触发之后初始化一个事件监听器,那么该事件监听器将不会被执行。这样是为什么在4.0之后AGS ForJS将很多的事件修改为Promise的原因之一。
Additional resources
- Understanding Deferreds and Promises in Dojo
- Dojo Deferreds and Promises
- Chaining Promises
- GeoNet - Keeping Promises
- JavaScript Promises
Arcade - expression language
Arcade是一个轻量级的表达式语言,它用于ArcGIS平台,和其他的表达式语言一样,可以执行数学计算和逻辑表达式。它被设计用来在ArcGIS平台中创建自定义的可视化和标记表达式。
Arcade与其他表达式和脚本语言不同的是,它包含几何函数。在Arcade的初始版本中,geometries can be created and referenced,在将来的版本中,更多的几何函数将会被添加进来辅助计算面积长度,执行简单的叠置操作。
语法
详细语法参考Arcade documentation。全局变量可能被用于Arcade表达式,用来访问外部的数据。全局变量包含外部数据(当脚本执行时被传递进来的)。$feature全局变量允许访问FeatureLayer中features的字段的值。字段值以下面的形式被引用:
1 |
Arcade仅仅在它能被来理解的context或者profile中被执行。有两种书写形式:
- single-line expressions
1 | renderer.valueExpression = "Round( ($feature.AGE_18UP / $feature.TOTAL_POP) * 100 )"; |
- multi-line expressions
AGS推荐将多行表达式写在<script>标签内,设置type为text/plain并且设置一个唯一的ID1
2
3<script type="text/plain" id="adult-population">
// place multi-line Arcade expression here
</script>
然后便可以获取该<script>的内容作为表达式的值了:
1 | renderer.valueExpression = document.getElementById("adult-population").text; |
Profiles
Arcade被设计用来为一些场景服务,一种场景即一个Arcade表达式能被理解和使用的context,在AGS For JS4.5中,Arcade支持3中场景:visualization, popups 和 labeling(目前labeling仅仅支持3D)。
- Visualization
在使用FeatureLayer创建可视化时,当依赖的value并非是FeatureLayer的一个实实在在的字段,而是要通过计算得到时,Arcade将非常有用。
在Visualization profile中,可以使用Arcade在运行时中去计算FeatureLayer或者SceneLayer的每一个feature,并且可以使用它们的值作为数据驱动可视化的基础。
为了使用Arcade表达式进行可视化,可以将Arcade表达式传递给ClassBreaksRenderer,UniqueValueRenderer的valueExpression属性或者其他的可视化变量:color,size,opacity, 和rotation。
Arcade supports creating visualizations for
FeatureLayerandSceneLayeronly.
Other layer types that acceptClassBreaksRendererandUniqueValueRenderer, such asMapImageLayer, do not support Arcade.
当Arcade被用于ClassBreaksRenderer或其他的可视化变量时,Arcade表达式计算得到的必须时一个数值。当Arcade被用于UniqueValueRenderer时Arcade表达式计算得到的可以是一个字符串也可以是一个数值。
如下场景,一个FeatureLayer的features表示US的县,每个features包含republicans,democrats,independents三者各自总数,现在要求使用不同的颜色来渲染每个县,颜色取决于该县中占统治地位的政党。当然我们可以先在数据中添加一个字段,用于存储每个县中占统治地位的政党,但是如果这个数据我们不能操作的话,这个办法就行不通了,Arcade便有了用武之地,它允许你写一个简单的表达式去计算出占统治地位的政党。然后将这个表达式传递给UniqueValueRenderer的valueExpression属性。
首先我们写出Arcade表达式:
1 | <script type="text/plain" id="winning-party"> |
然后引用该表达式:
1 | // Assign the expression to the `valueExpression` property and |
在用透明度表示该政党占统治地位的程度:
同样首先来写出Arcade表达式:
1 | <script type="text/plain" id="strength"> |
然后引用该表达式:
1 | // Assign the expression to the `valueExpression` property and |
- Popups
Arcade表达式同样也可以被用于PopupTemplate的content属性。和visualization profile类似,它适用的场景也是当你要展示的数值不是作为一个属性值存在于FeatureLayer中。
在Popus中使用Arcade表达式,必须将它设置到PopupTemplate的expressionInfos属性中并且为其分配name和title。
1 | layer.popupTemplate = { |
如上面的示例,将Arcade表达式设置到expressionInfos属性之后,便可以在content中使用{expession/expression-name}占位符模板来引用Arcade表达式的返回值。
同样可以在fieldInfos属性中设置Arcade expressions,只是在PopupTemplate的content中设置fieldName属性为expression/expression-name。
1 | layer.popupTemplate = { |
- Labeling
Known Limitations:
Labeling is currently only supported in 3D SceneViews. Support for labeling in 2D MapViews will be added in a future release.
必须为图层的labelingInfo添加至少一个esri/layers/support/LabelClass,并且设置labelsVisible属性为true。传递给LabelClass的 labelExpressionInfo的expression的 Arcade expression返回值必须是字符串。
1 | // returns the value of a field in the layer |
Autocasting
Autocasting只能用于类的属性,它允许我们不require相应的模块直接以对象字面量的形式传递。之所以只能是类的属性是因为类的属性的类型是已知的,固定的。
1 | require([ |
loadable pattern
layers, maps, portal items, tasks等等通常依赖remote services或者硬盘中的数据集来初始化它的状态的Resources。loadable pattern就是专门为这种场景设置的。
Load status
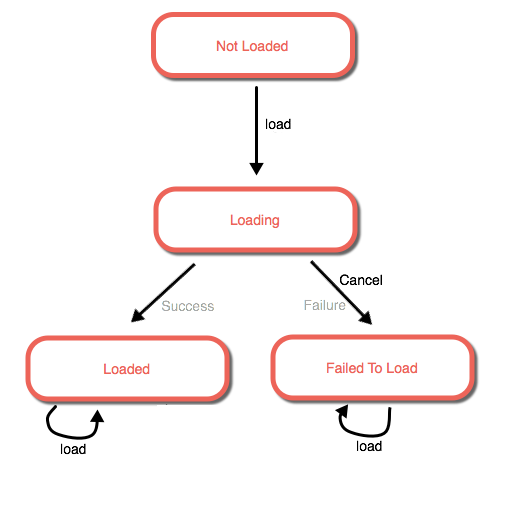
Loadable接口包括了listeners,使得监控loadable resource的状态,显示进度,当状态改变执行相应的操作,变得更加容易。
当调用load方法后,资源开始异步加载元数据,这是load状态从not-loaded变为loading。当异步操作成功后,回调函数变被执行。当操作遇见错误,回调函数的error参数将被添加,同时loadStatus 被设置为failed,如果操作成功,error参数为null,loadStatus 被设置为loaded,这意味着资源的元数据加载完成正在准备初始化。
很多时候,程序不同的地方共享这相同的资源,如,图例组件和TOC组件都访问相同的layer,并且它们都要访问layer的属性以填充它们的UI。load()支持多个”listeners”以简化这种场景。它可以同时和重复的被调用,但是只访问元数据一次。
当load被调用了,并且如果操作已经完成(loaded或者failed),callback立即被触发,并传入操作的结果。
Cascading load dependencies
1 | // create a Map loaded from a webmap |


